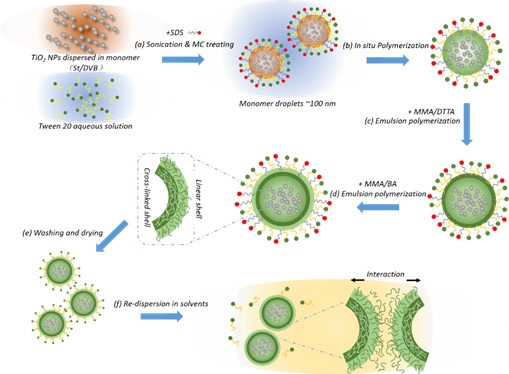
A Facile Construction of Core-Double Shell Architecture to Assist Re-dispersion of Hybrid Nanoparticles
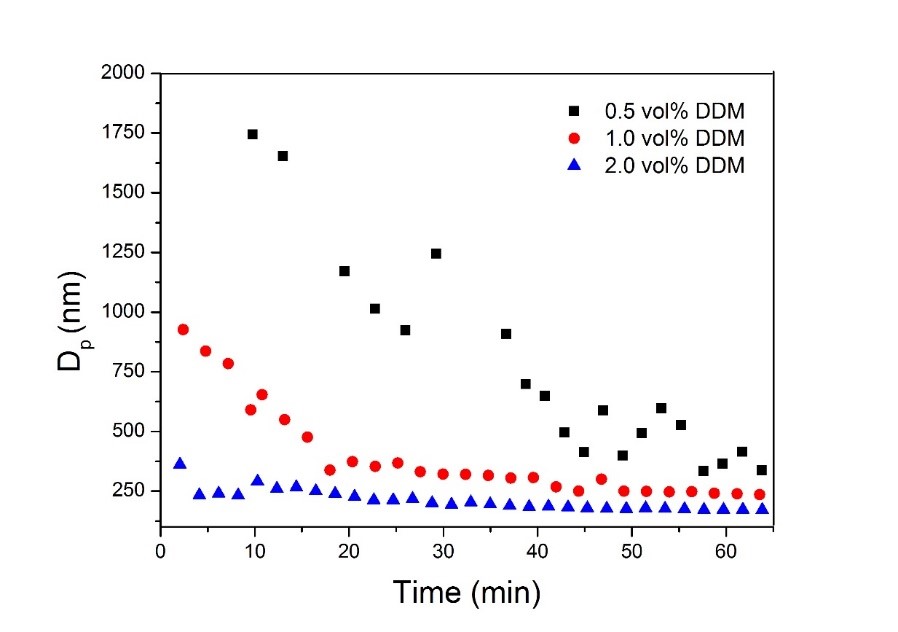
Fast and stable re-dispersion of inorganic nanoparticles into organic solvent or matrix is essential for developing hybrid materials with excellent performance applied in many technological fields. The major challenge in the re-dispersion process arises from the physicochemical incompatibility between inorganic and organic components which leads to aggregation or phase separation. Inspired by conventional strategy of surface modification, we propose a core-double shell architecture to effectively assist re-dispersion of nanoparticles and demonstrate the advantages in improving colloidal stability. This work covers the synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles embedded in polymer matrix and the encapsulation by the polymeric double shells fabricated through emulsion polymerization, and compares the impact of outermost shell chain property on dispersion kinetics. The thermoresponsive behaviors of nanoparticles with different chain length (tuned by varying amount of chain transfer agent DDM) in outermost shell have been investigated in details, confirming that the shell property contributes to fast re-dispersion.
Contact Person: Lu Jin